References
![]() For additional information, refer to the following resources:
For additional information, refer to the following resources:
-
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Product Documentation, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm
Cisco Systems, Inc., Product Documentation, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Solution Reference Network Design Guides home page, http://www.cisco.com/go/srnd/
Cisco Systems, Inc., Solution Reference Network Design Guides home page, http://www.cisco.com/go/srnd/ -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Enterprise QoS Solution Reference Network Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns432/c649/ccmigration_09186a008049b062.pdf
Cisco Systems, Inc., Enterprise QoS Solution Reference Network Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns432/c649/ccmigration_09186a008049b062.pdf -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Frame Relay technical overview, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/frame.htm
Cisco Systems, Inc., Frame Relay technical overview, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/frame.htm -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., MPLS and Tag Switching technical overview, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/mpls_tsw.htm
Cisco Systems, Inc., MPLS and Tag Switching technical overview, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/ito_doc/mpls_tsw.htm -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Enterprise Architectures, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns517/networking_solutions_market_segment_solutions_home.html
Cisco Systems, Inc., Enterprise Architectures, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns517/networking_solutions_market_segment_solutions_home.html -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco product index for routers, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/routers/index.html
Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco product index for routers, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/routers/index.html -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco product index for switches, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/index.html
Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco product index for switches, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/index.html -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco Feature Navigator, http://www.cisco.com/go/fn
Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco Feature Navigator, http://www.cisco.com/go/fn -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco IOS Packaging: Introduction, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps5460/index.html
Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco IOS Packaging: Introduction, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/iosswrel/ps5460/index.html -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Business Ready Branch Solutions for Enterprise and Small Offices—Reference Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns656/c649/cdccont_0900aecd80488134.pdf
Cisco Systems, Inc., Business Ready Branch Solutions for Enterprise and Small Offices—Reference Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns656/c649/cdccont_0900aecd80488134.pdf -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/solution/designex.pdf
Cisco Systems, Inc., LAN Baseline Architecture Branch Office Network Reference Design Guide, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/solution/designex.pdf -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., LAN Baseline Architecture Overview—Branch Office Network, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/solution/lanovext.pdf
Cisco Systems, Inc., LAN Baseline Architecture Overview—Branch Office Network, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/solution/lanovext.pdf -
 Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco Business Ready Teleworker Architecture, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns430/c654/cdccont_0900aecd800df177.pdf
Cisco Systems, Inc., Cisco Business Ready Teleworker Architecture, http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/netsol/ns430/c654/cdccont_0900aecd800df177.pdf
Case Study: ACMC Hospital Network WAN Design
![]() This case study is a continuation of the ACMC Hospital case study introduced in Chapter 2, “Applying a Methodology to Network Design.”
This case study is a continuation of the ACMC Hospital case study introduced in Chapter 2, “Applying a Methodology to Network Design.”
![]() In this case study, you create a high-level design for the WAN portions of the ACMC Hospital network.
In this case study, you create a high-level design for the WAN portions of the ACMC Hospital network.
 Case Study Additional Information
Case Study Additional Information
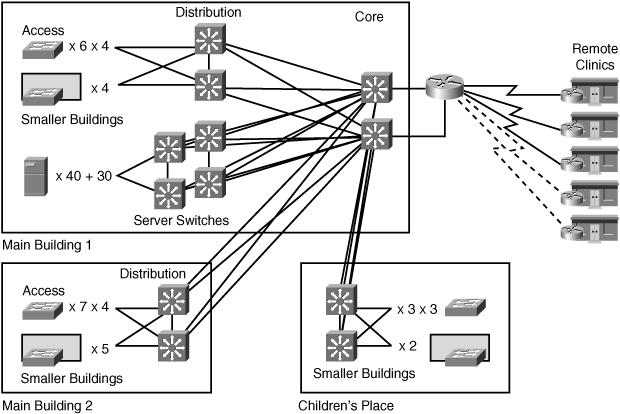
![]() Figure 5-30 shows the existing WAN links and the planned campus infrastructure.
Figure 5-30 shows the existing WAN links and the planned campus infrastructure.
Business Factors
![]() The ACMC Hospital CIO realizes that WAN performance to the remote clinics is poor and that some new applications will require more bandwidth. These applications include programs that allow doctors at the central site to access medical images, such as digital X-rays, stored locally at the clinics. The CIO wants all the remote sites to have the same type of access.
The ACMC Hospital CIO realizes that WAN performance to the remote clinics is poor and that some new applications will require more bandwidth. These applications include programs that allow doctors at the central site to access medical images, such as digital X-rays, stored locally at the clinics. The CIO wants all the remote sites to have the same type of access.
![]() The CIO wants to implement a long-term, cost-effective solution that allows high-bandwidth application deployment on the network and that allows for growth for the next two to five years. The CIO also wants to simplify planning, pricing, and deployment of future applications.
The CIO wants to implement a long-term, cost-effective solution that allows high-bandwidth application deployment on the network and that allows for growth for the next two to five years. The CIO also wants to simplify planning, pricing, and deployment of future applications.
Technical Factors
![]() There is no data about the bandwidth requirements of the new applications. Lab testing would provide better data, but ACMC does not have the time or money for testing. The CIO knows that because TCP adjusts to use the available bandwidth, such that when congestion occurs, there is no way to know how much bandwidth the present applications could ideally use unless extensive lab testing is done.
There is no data about the bandwidth requirements of the new applications. Lab testing would provide better data, but ACMC does not have the time or money for testing. The CIO knows that because TCP adjusts to use the available bandwidth, such that when congestion occurs, there is no way to know how much bandwidth the present applications could ideally use unless extensive lab testing is done.
![]() You discover that your site contact initially supplied you with an out-of-date network diagram. The hospital upgraded the 56 kbps links to 128 kbps a year ago and upgraded the WAN bandwidth at the largest clinic to 256 kbps last month. Therefore, the following is the current state of the WAN links:
You discover that your site contact initially supplied you with an out-of-date network diagram. The hospital upgraded the 56 kbps links to 128 kbps a year ago and upgraded the WAN bandwidth at the largest clinic to 256 kbps last month. Therefore, the following is the current state of the WAN links:
-
 The connection to the largest remote clinic now runs at 256 kbps.
The connection to the largest remote clinic now runs at 256 kbps. -
 The connections to two other remote clinics were upgraded from 56 kbps to 128 kbps.
The connections to two other remote clinics were upgraded from 56 kbps to 128 kbps. -
 The two remaining remote clinics have 56-kbps dialup connectivity.
The two remaining remote clinics have 56-kbps dialup connectivity.
![]() The increased WAN bandwidth you recommend should last for two to five years.
The increased WAN bandwidth you recommend should last for two to five years.
![]() For situations in which you cannot really determine how much WAN bandwidth is needed, one way to proceed is to multiply current traffic levels by a value of 1.5 or 2 per year. However, if the customer does not want to be concerned with needing even more bandwidth in the near future, multiply by bigger numbers. If you expect unknown applications to be added to the network, multiply by even bigger numbers. In this case study, assume that all clinics are to be upgraded to at least T1 access speed. (Pricing structures in many areas might even favor a full T1 over fractional T1 links.)
For situations in which you cannot really determine how much WAN bandwidth is needed, one way to proceed is to multiply current traffic levels by a value of 1.5 or 2 per year. However, if the customer does not want to be concerned with needing even more bandwidth in the near future, multiply by bigger numbers. If you expect unknown applications to be added to the network, multiply by even bigger numbers. In this case study, assume that all clinics are to be upgraded to at least T1 access speed. (Pricing structures in many areas might even favor a full T1 over fractional T1 links.)
 Case Study Questions
Case Study Questions
![]() Complete the following steps:
Complete the following steps:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|

2 comments
I feel really happy to have seen your webpage and look forward to so many more entertaining times reading here. Thanks once more for all the details.
Great post keep on posting
Data science Course Training in Chennai |Best Data Science Training Institute in Chennai
RPA Course Training in Chennai |Best RPA Training Institute in Chennai
AWS Course Training in Chennai |Best AWS Training Institute in Chennai
Devops Course Training in Chennai |Best Devops Training Institute in Chennai
Selenium Course Training in Chennai |Best Selenium Training Institute in Chennai
Java Course Training in Chennai | Best Java Training Institute in Chennai
Ansible Training chennai | Ansible training institute chennai
Best software training institute in Chennai. Make your career development the best by learning software courses.
best rpa training in chennai
uipath training in chennai
cloud computing courses in chennai
Post a Comment