References
![]() For additional information, refer to these resources:
For additional information, refer to these resources:
-
 Echo Analysis for Voice over IP, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/tech/tk652/tk701/technologies_white_paper09186a00800d6b68.shtml.
Echo Analysis for Voice over IP, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/tech/tk652/tk701/technologies_white_paper09186a00800d6b68.shtml.Note  You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this document.
You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this document. -
 Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.4, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios124/124cg/hqos_c/index.htm.
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.4, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios124/124cg/hqos_c/index.htm. -
 Introduction to voice, including telephony signaling documents, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk652/tsd_technology_support_category_home.html.
Introduction to voice, including telephony signaling documents, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk652/tsd_technology_support_category_home.html. -
 Traffic Analysis for Voice over IP, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/intsolns/voipsol/ta_isd.htm.
Traffic Analysis for Voice over IP, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/cisintwk/intsolns/voipsol/ta_isd.htm. -
 Understanding Delay in Packet Voice Networks, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/voip/delay-details.html.
Understanding Delay in Packet Voice Networks, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/voip/delay-details.html. -
 Voice Network Signaling and Control, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/net_signal_control.html.
Voice Network Signaling and Control, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/net_signal_control.html. -
 Waveform Coding Techniques, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/waveform_coding.html#subrstsix.
Waveform Coding Techniques, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/waveform_coding.html#subrstsix. -
 Erlang tables on Westbay Engineers Limited Home Page, http://www.erlang.com/.
Erlang tables on Westbay Engineers Limited Home Page, http://www.erlang.com/. -
 Szigeti and Hattingh, End-to-End QoS Network Design: Quality of Service in LANs, WANs, and VPNs, Indianapolis, Cisco Press, 2004.
Szigeti and Hattingh, End-to-End QoS Network Design: Quality of Service in LANs, WANs, and VPNs, Indianapolis, Cisco Press, 2004. -
 Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CallManager): Introduction, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/index.html.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CallManager): Introduction, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/index.html. -
 Cisco Unified Communications SRND Based on Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/products_implementation_design_guide_book09186a00806492bb.html.
Cisco Unified Communications SRND Based on Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/products_implementation_design_guide_book09186a00806492bb.html. -
 Understanding Codecs: Complexity, Hardware Support, MOS, and Negotiation, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk1077/technologies_tech_note09186a00800b6710.shtml.
Understanding Codecs: Complexity, Hardware Support, MOS, and Negotiation, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk1077/technologies_tech_note09186a00800b6710.shtml. -
 Davidson, J., and J. Peters. Voice over IP Fundamentals. Indianapolis: Cisco Press, 2000.
Davidson, J., and J. Peters. Voice over IP Fundamentals. Indianapolis: Cisco Press, 2000. -
 Voice Network Signaling and Control, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/net_signal_control.html.
Voice Network Signaling and Control, http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/signalling/net_signal_control.html. -
 Voice over IP—Per-Call Bandwidth Consumption, http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/788/pkt-voice-general/bwidth_consume.html.
Voice over IP—Per-Call Bandwidth Consumption, http://www.cisco.com/warp/customer/788/pkt-voice-general/bwidth_consume.html.Note  You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this document.
You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this document. -
 Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios124/124tcg/vcl.htm.
Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library, http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios124/124tcg/vcl.htm. -
 High-Density Packet Voice/Fax Digital Signal Processor Module, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/univgate/ps501/products_data_sheet0900aecd80458049.html.
High-Density Packet Voice/Fax Digital Signal Processor Module, http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/univgate/ps501/products_data_sheet0900aecd80458049.html. -
 Cisco Voice Codec Bandwidth Calculator, http://tools.cisco.com/Support/VBC/do/CodecCalc1.do.
Cisco Voice Codec Bandwidth Calculator, http://tools.cisco.com/Support/VBC/do/CodecCalc1.do.Note  You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this calculator.
You must be a registered user on http://www.cisco.com/ to access this calculator.
Case Study: ACMC Hospital Network Voice Design
![]() This case study is a continuation of the ACMC Hospital case study introduced in Chapter 2.
This case study is a continuation of the ACMC Hospital case study introduced in Chapter 2.
![]() In this case study you create a high-level voice design for the ACMC Hospital network.
In this case study you create a high-level voice design for the ACMC Hospital network.
 Case Study Additional Information
Case Study Additional Information
![]() The ACMC staff wants to replace its PBX and key systems and is eager to achieve cost reduction while providing better service to remote clinics. The replacement system needs to offer at least as many features as the present system. The staff is also very interested in unified voice-mail services for busy doctors and the potential for using phones with web-based menus as part of a quality care system.
The ACMC staff wants to replace its PBX and key systems and is eager to achieve cost reduction while providing better service to remote clinics. The replacement system needs to offer at least as many features as the present system. The staff is also very interested in unified voice-mail services for busy doctors and the potential for using phones with web-based menus as part of a quality care system.
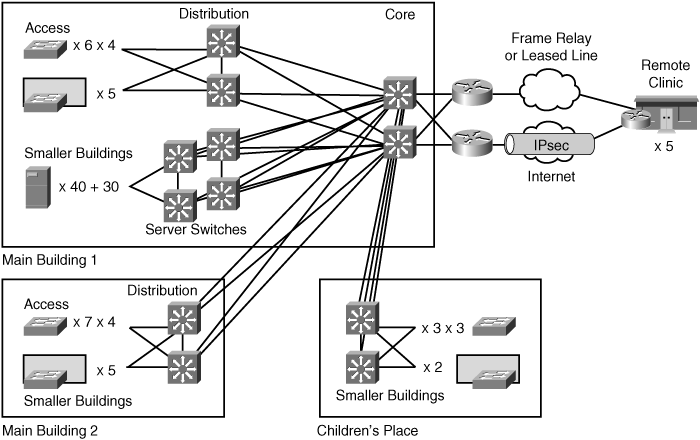
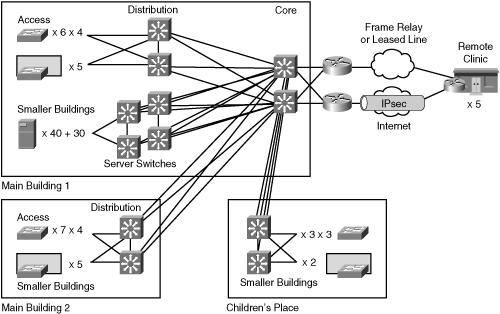
![]() Current features include standard PBX features, call conferencing, voice mail, and local calls. Remote clinics currently use some form of key system or remote PBX shelf with limited features. Figure 8-38 summarizes the ACMC design up to this point for your reference.
Current features include standard PBX features, call conferencing, voice mail, and local calls. Remote clinics currently use some form of key system or remote PBX shelf with limited features. Figure 8-38 summarizes the ACMC design up to this point for your reference.
 Case Study Questions
Case Study Questions
![]() Complete the following steps:
Complete the following steps:
|
| |||||||
|
| |||||||
|
| |||||||
|
| |||||||
|
|

0 comments
Post a Comment