Network Security Solutions
![]() This section discusses how security is integrated in Cisco network devices and describes designing network security solutions for enterprise networks.
This section discusses how security is integrated in Cisco network devices and describes designing network security solutions for enterprise networks.
 Integrated Security Within Network Devices
Integrated Security Within Network Devices
![]() The section explains the security features integrated in Cisco network devices. To design and implement a secure network, it is necessary to integrate security in every part of the network environment. Cisco network devices supporting integrated security include the following:
The section explains the security features integrated in Cisco network devices. To design and implement a secure network, it is necessary to integrate security in every part of the network environment. Cisco network devices supporting integrated security include the following:
-
 Cisco IOS routers
Cisco IOS routers -
 Security appliances, including
Security appliances, including-
 VPN concentrators
VPN concentrators -
 Cisco PIX security appliances
Cisco PIX security appliances -
 ASAs
ASAs
-
-
 Catalyst services modules
Catalyst services modules -
 Endpoint security solutions
Endpoint security solutions
![]() The following sections describe these devices.
The following sections describe these devices.
Cisco IOS Router Security
![]() Devices based on Cisco IOS software incorporate various security features to create an integrated and scalable network.
Devices based on Cisco IOS software incorporate various security features to create an integrated and scalable network.
![]() The Cisco IOS Firewall is a security-specific option for Cisco IOS software that provides integrated network security with robust stateful firewall functionality for network perimeters. The Cisco IOS Firewall gives enterprises and small and medium businesses a very cost-effective option, in terms of both initial capital investment and continuing administrative costs. The Cisco IOS Firewalls help businesses guarantee network uptime and security by protecting customer networks from network and application layer attacks, viruses, and worms, and providing effective control of application traffic flowing through the network. The Cisco IOS Firewall offers sophisticated security and policy-enforcement services for connections within an organization (intranet) and between partner networks (extranets), as well as for securing Internet connectivity for teleworker and branch offices.
The Cisco IOS Firewall is a security-specific option for Cisco IOS software that provides integrated network security with robust stateful firewall functionality for network perimeters. The Cisco IOS Firewall gives enterprises and small and medium businesses a very cost-effective option, in terms of both initial capital investment and continuing administrative costs. The Cisco IOS Firewalls help businesses guarantee network uptime and security by protecting customer networks from network and application layer attacks, viruses, and worms, and providing effective control of application traffic flowing through the network. The Cisco IOS Firewall offers sophisticated security and policy-enforcement services for connections within an organization (intranet) and between partner networks (extranets), as well as for securing Internet connectivity for teleworker and branch offices.
![]() The Cisco IOS IPS is an inline, deep packet inspection–based feature that enables Cisco IOS software to effectively mitigate a wide range of network attacks. As a core facet of the Cisco Self-Defending Network, the Cisco IOS IPS enables the network to defend itself with the intelligence to accurately identify, classify, and stop or block malicious or damaging traffic in real time. The Cisco IOS IPS operates by loading a set of attack signatures on the router. To assist users in signature selection, Cisco provides prebuilt signature definition files that contain high-fidelity signatures based on the memory available on a router. Registered users on http://www.cisco.com/ with a Cisco service agreement can download the latest version of these files and the complete set of Cisco IPS signatures in Cisco IOS IPS signature definition files. The Cisco IOS IPS complements the Cisco IOS Firewall and VPN solutions for superior threat protection at all entry points into the network.
The Cisco IOS IPS is an inline, deep packet inspection–based feature that enables Cisco IOS software to effectively mitigate a wide range of network attacks. As a core facet of the Cisco Self-Defending Network, the Cisco IOS IPS enables the network to defend itself with the intelligence to accurately identify, classify, and stop or block malicious or damaging traffic in real time. The Cisco IOS IPS operates by loading a set of attack signatures on the router. To assist users in signature selection, Cisco provides prebuilt signature definition files that contain high-fidelity signatures based on the memory available on a router. Registered users on http://www.cisco.com/ with a Cisco service agreement can download the latest version of these files and the complete set of Cisco IPS signatures in Cisco IOS IPS signature definition files. The Cisco IOS IPS complements the Cisco IOS Firewall and VPN solutions for superior threat protection at all entry points into the network.
![]() The Cisco IOS IPsec functionality provides network data encryption at the IP packet level, resulting in a robust, standards-based security solution. IPsec provides data confidentiality, data authentication, and antireplay services, and it is the only way to implement secure VPNs. Organizations combine IPsec with other Cisco IOS software functionality to build scalable, robust, and secure QoS-aware VPNs.
The Cisco IOS IPsec functionality provides network data encryption at the IP packet level, resulting in a robust, standards-based security solution. IPsec provides data confidentiality, data authentication, and antireplay services, and it is the only way to implement secure VPNs. Organizations combine IPsec with other Cisco IOS software functionality to build scalable, robust, and secure QoS-aware VPNs.
![]() The Cisco IOS software trust and identity services include core technologies that enable network traffic security: AAA, PKI, SSH, SSL, and 802.1X. The Cisco IOS AAA is an architectural framework for configuring a set of three independent security functions in a consistent manner, providing a modular way to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting services on a router or access server. PKI provides strong and robust authentication, authorization, confidentiality, and nonrepudiation for e-business and e-commerce applications.
The Cisco IOS software trust and identity services include core technologies that enable network traffic security: AAA, PKI, SSH, SSL, and 802.1X. The Cisco IOS AAA is an architectural framework for configuring a set of three independent security functions in a consistent manner, providing a modular way to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting services on a router or access server. PKI provides strong and robust authentication, authorization, confidentiality, and nonrepudiation for e-business and e-commerce applications.
![]() Cisco ISRs support the following additional options to enhance network security:
Cisco ISRs support the following additional options to enhance network security:
-
 Built-in VPN acceleration: The built-in, hardware-based encryption acceleration offloads the VPN processes to provide increased VPN throughput with minimal impact on the router CPU.
Built-in VPN acceleration: The built-in, hardware-based encryption acceleration offloads the VPN processes to provide increased VPN throughput with minimal impact on the router CPU. -
 Secure voice: Packet voice digital signal processor (DSP) modules (PVDM) for the DSP slots in ISRs provide conferencing, transcoding, and secure voice features. The Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol encrypts the voice payload, leaving the header in cleartext to support QoS and other features.
Secure voice: Packet voice digital signal processor (DSP) modules (PVDM) for the DSP slots in ISRs provide conferencing, transcoding, and secure voice features. The Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol encrypts the voice payload, leaving the header in cleartext to support QoS and other features. -
 High-performance advanced integration module (AIM): The VPN and encryption AIMs are used for aggregation-type applications, such as DMVPNs, in which large numbers of remote VPN tunnels are required. The VPN and encryption AIMs support 3DES and AES and boost router encryption and compression performance.
High-performance advanced integration module (AIM): The VPN and encryption AIMs are used for aggregation-type applications, such as DMVPNs, in which large numbers of remote VPN tunnels are required. The VPN and encryption AIMs support 3DES and AES and boost router encryption and compression performance. -
 Cisco IDS Network Module for the Cisco 2600, 2800, 3600, 3700, and 3800 Routers: The Cisco IDS Network Module (NM-CIDS) includes innovative technologies, including correlation and validation tools, which take preventive actions on a broader range of threats and greatly reduce the risk of dropping legitimate traffic.
Cisco IDS Network Module for the Cisco 2600, 2800, 3600, 3700, and 3800 Routers: The Cisco IDS Network Module (NM-CIDS) includes innovative technologies, including correlation and validation tools, which take preventive actions on a broader range of threats and greatly reduce the risk of dropping legitimate traffic. -
 Cisco 2600/2800/3600/3700/3800 Series Content Engine Module: The Cisco Content Engine Network Module provides a router-integrated application and content networking system. Available configurations include a 40-GB hard disk or an 80-GB internal hard disk.
Cisco 2600/2800/3600/3700/3800 Series Content Engine Module: The Cisco Content Engine Network Module provides a router-integrated application and content networking system. Available configurations include a 40-GB hard disk or an 80-GB internal hard disk. -
 Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM): The Cisco NAM analyzes traffic flows for applications, hosts, conversations, and IP-based services such as QoS and VoIP. It also collects exported NetFlow data to provide broad application-level visibility.
Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM): The Cisco NAM analyzes traffic flows for applications, hosts, conversations, and IP-based services such as QoS and VoIP. It also collects exported NetFlow data to provide broad application-level visibility.
| Note |
|
| Note |
|
Security Appliances
![]() This section introduces Cisco security appliances.
This section introduces Cisco security appliances.
VPN Concentrators
![]() The Cisco VPN 3000 Series concentrators are remote-access VPN devices that provide enterprises with IPsec- and SSL-based VPN connectivity. The centralized architecture provides ease of management and implementation in deployments that require detailed access controls for numerous deployment scenarios with diverse user communities, including mobile workers, telecommuters, and extranet users.
The Cisco VPN 3000 Series concentrators are remote-access VPN devices that provide enterprises with IPsec- and SSL-based VPN connectivity. The centralized architecture provides ease of management and implementation in deployments that require detailed access controls for numerous deployment scenarios with diverse user communities, including mobile workers, telecommuters, and extranet users.
Cisco PIX Security Appliances
![]() The Cisco PIX 500 Series security appliances deliver rich application and protocol inspection, robust user and application policy enforcement, multivector attack protection, and secure connectivity services in cost-effective, easy-to-deploy solutions. Ranging from the compact, plug-and-play desktop Cisco PIX 501 security appliance for SOHOs to the modular gigabit Cisco PIX 535 security appliance with superior investment protection for enterprise and service-provider environments, Cisco PIX 500 Series security appliances provide comprehensive security, performance, and reliability for network environments of all sizes.
The Cisco PIX 500 Series security appliances deliver rich application and protocol inspection, robust user and application policy enforcement, multivector attack protection, and secure connectivity services in cost-effective, easy-to-deploy solutions. Ranging from the compact, plug-and-play desktop Cisco PIX 501 security appliance for SOHOs to the modular gigabit Cisco PIX 535 security appliance with superior investment protection for enterprise and service-provider environments, Cisco PIX 500 Series security appliances provide comprehensive security, performance, and reliability for network environments of all sizes.
ASAs
![]() The Cisco ASA 5500 Series ASAs are high-performance, multifunction security appliances delivering converged firewall, IPS, network antivirus, and VPN services. As a key component of the Cisco Self-Defending Network, these appliances provide proactive threat mitigation that stops attacks before they spread through the network, control network activity and application traffic, and deliver flexible VPN connectivity while remaining cost-effective and easy to manage.
The Cisco ASA 5500 Series ASAs are high-performance, multifunction security appliances delivering converged firewall, IPS, network antivirus, and VPN services. As a key component of the Cisco Self-Defending Network, these appliances provide proactive threat mitigation that stops attacks before they spread through the network, control network activity and application traffic, and deliver flexible VPN connectivity while remaining cost-effective and easy to manage.
![]() Compared to the Cisco PIX security appliances, the ASAs offer additional services, such as IPS functionality, adaptive threat defense capabilities, application security, Anti-X defenses, integration with Cisco WebVPN Services modules, and AIMs to enhance the appliance’s processing capabilities.
Compared to the Cisco PIX security appliances, the ASAs offer additional services, such as IPS functionality, adaptive threat defense capabilities, application security, Anti-X defenses, integration with Cisco WebVPN Services modules, and AIMs to enhance the appliance’s processing capabilities.
IPSs
![]() The Cisco IPS solution combines passive IDS with inline IPS. The Cisco IPS appliances offer comprehensive proactive protection of the network through their capability to collaborate with other network security resources. These appliances support multivector threat identification to protect the network from policy violations, vulnerability exploitations, and anomalous activity through detailed inspection of traffic in Layers 2 through 7.
The Cisco IPS solution combines passive IDS with inline IPS. The Cisco IPS appliances offer comprehensive proactive protection of the network through their capability to collaborate with other network security resources. These appliances support multivector threat identification to protect the network from policy violations, vulnerability exploitations, and anomalous activity through detailed inspection of traffic in Layers 2 through 7.
![]() Cisco IPS 4200 Series sensors offer significant network protection by helping detect, classify, and stop threats, including worms, spyware, adware, network viruses, and application abuse. Using Cisco IPS Sensor Software Version 5.1, the Cisco IPS solution combines inline IPS with innovative technologies that improve accuracy so that more threats can be stopped without the risk of dropping legitimate network traffic. This software includes enhanced detection capabilities and improved scalability, resiliency, and performance features.
Cisco IPS 4200 Series sensors offer significant network protection by helping detect, classify, and stop threats, including worms, spyware, adware, network viruses, and application abuse. Using Cisco IPS Sensor Software Version 5.1, the Cisco IPS solution combines inline IPS with innovative technologies that improve accuracy so that more threats can be stopped without the risk of dropping legitimate network traffic. This software includes enhanced detection capabilities and improved scalability, resiliency, and performance features.
![]() The available sensors support bandwidths up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) and include the following:
The available sensors support bandwidths up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) and include the following:
-
 The Cisco IPS 4215 sensor accurately investigates and protects up to 65 Mbps of traffic and is suitable for multiple T1/E1 and T3 environments.
The Cisco IPS 4215 sensor accurately investigates and protects up to 65 Mbps of traffic and is suitable for multiple T1/E1 and T3 environments. -
 The Cisco IPS 4240 sensor, at 250 Mbps, can be deployed to provide protection in switched environments with multiple T3 subnets. With the support of multiple 10/100/1000 interfaces, it can also be deployed on partially utilized gigabit links or fully saturated full-duplex 100-Mbps environments.
The Cisco IPS 4240 sensor, at 250 Mbps, can be deployed to provide protection in switched environments with multiple T3 subnets. With the support of multiple 10/100/1000 interfaces, it can also be deployed on partially utilized gigabit links or fully saturated full-duplex 100-Mbps environments. -
 The Cisco 4240-DC sensor is based on the IPS 4240 sensor but supports DC power. The IPS 4240-DC is Network Equipment Building System (NEBS)–compliant and can be deployed in environments that have specific requirements pertaining to NEBS Level 3 compliance.
The Cisco 4240-DC sensor is based on the IPS 4240 sensor but supports DC power. The IPS 4240-DC is Network Equipment Building System (NEBS)–compliant and can be deployed in environments that have specific requirements pertaining to NEBS Level 3 compliance.Note  NEBS is a set of standards for telecommunications equipment that specifies the equipment’s operation with respect to a variety of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration.
NEBS is a set of standards for telecommunications equipment that specifies the equipment’s operation with respect to a variety of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration. -
 The Cisco IPS 4255 sensor delivers 500 Mbps of performance. It can be used to protect partially utilized gigabit subnets and traffic traversing switches being used to aggregate traffic from many subnets.
The Cisco IPS 4255 sensor delivers 500 Mbps of performance. It can be used to protect partially utilized gigabit subnets and traffic traversing switches being used to aggregate traffic from many subnets. -
 The Cisco IPS 4260 sensor delivers 1 Gbps of protection performance. It can be used to protect both gigabit subnets and aggregated traffic traversing switches from multiple subnets. This purpose-built device supports both copper and fiber environments, providing deployment flexibility.
The Cisco IPS 4260 sensor delivers 1 Gbps of protection performance. It can be used to protect both gigabit subnets and aggregated traffic traversing switches from multiple subnets. This purpose-built device supports both copper and fiber environments, providing deployment flexibility.
Catalyst Services Modules
![]() The following are various security-related modules for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switching platform (and some are also for the Cisco 7600 Series routers):
The following are various security-related modules for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switching platform (and some are also for the Cisco 7600 Series routers):
-
 Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series FWSM: The Cisco FWSM is a high-speed, integrated firewall module for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. Up to four Cisco FWSMs can be installed in a single chassis, providing scalability up to 20 Gbps per chassis. The Cisco FWSM includes many advanced features, such as multiple security contexts at both the routed level and in bridging mode, helping reduce cost and operational complexity while managing multiple firewalls from the same management platform.
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series FWSM: The Cisco FWSM is a high-speed, integrated firewall module for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. Up to four Cisco FWSMs can be installed in a single chassis, providing scalability up to 20 Gbps per chassis. The Cisco FWSM includes many advanced features, such as multiple security contexts at both the routed level and in bridging mode, helping reduce cost and operational complexity while managing multiple firewalls from the same management platform. -
 Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Intrusion Detection System Services module 2 (IDSM-2): The Cisco IDSM-2 is part of the Cisco IPS that works in concert with the other components to efficiently protect the data infrastructure. It supports both inline (IPS) mode and passive operation (IDS). Up to 500 Mbps of IDS and IPS inspection provides high-speed packet examination and allows for protection of a wider variety of networks and traffic.
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Intrusion Detection System Services module 2 (IDSM-2): The Cisco IDSM-2 is part of the Cisco IPS that works in concert with the other components to efficiently protect the data infrastructure. It supports both inline (IPS) mode and passive operation (IDS). Up to 500 Mbps of IDS and IPS inspection provides high-speed packet examination and allows for protection of a wider variety of networks and traffic. -
 Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series SSL Services module: The Cisco SSL Services module is an integrated services module for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. It offloads processor-intensive tasks related to securing traffic with SSL, increases the number of secure connections supported by a website, and reduces the operational complexity of high-performance web server farms. Up to four Cisco SSL Services modules can be installed in each chassis.
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series SSL Services module: The Cisco SSL Services module is an integrated services module for the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. It offloads processor-intensive tasks related to securing traffic with SSL, increases the number of secure connections supported by a website, and reduces the operational complexity of high-performance web server farms. Up to four Cisco SSL Services modules can be installed in each chassis. -
 Cisco IPsec VPN Shared Port Adapter (SPA): The Cisco IPsec VPN SPA delivers scalable and cost-effective VPN performance for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. Using the Cisco Services SPA Carrier-400, each slot of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 switch or Cisco 7600 router can support up to two Cisco IPsec VPN SPAs. Although the Cisco IPsec VPN SPA does not have physical WAN or LAN interfaces, it takes advantage of the breadth of LAN and WAN interfaces of each of the platforms.
Cisco IPsec VPN Shared Port Adapter (SPA): The Cisco IPsec VPN SPA delivers scalable and cost-effective VPN performance for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers. Using the Cisco Services SPA Carrier-400, each slot of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 switch or Cisco 7600 router can support up to two Cisco IPsec VPN SPAs. Although the Cisco IPsec VPN SPA does not have physical WAN or LAN interfaces, it takes advantage of the breadth of LAN and WAN interfaces of each of the platforms. -
 Cisco Catalyst 6500/Cisco 7600 Traffic Anomaly Detector module: The Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module uses behavioral analysis and attack recognition technology to proactively detect and identify all types of online assaults. By constantly monitoring traffic destined for a protected device, such as a web or e-commerce server, the Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module compiles detailed profiles that indicate how individual devices behave under normal operating conditions. If the Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module detects any per-flow deviations from the profile, it considers the anomalous behavior a potential attack and responds based on user preference—by sending an operator alert to initiate a manual response, by notifying a management system, or by launching the Cisco Anomaly Guard Module to immediately begin mitigation services.
Cisco Catalyst 6500/Cisco 7600 Traffic Anomaly Detector module: The Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module uses behavioral analysis and attack recognition technology to proactively detect and identify all types of online assaults. By constantly monitoring traffic destined for a protected device, such as a web or e-commerce server, the Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module compiles detailed profiles that indicate how individual devices behave under normal operating conditions. If the Cisco Traffic Anomaly Detector module detects any per-flow deviations from the profile, it considers the anomalous behavior a potential attack and responds based on user preference—by sending an operator alert to initiate a manual response, by notifying a management system, or by launching the Cisco Anomaly Guard Module to immediately begin mitigation services. -
 Cisco Catalyst 6500/Cisco 7600 Anomaly Guard module: A single Cisco Anomaly Guard module allows the platform to process attack traffic at gigabit-per-second line rates. The Cisco Anomaly Guard module employs a unique on-demand deployment model, diverting and scrubbing only traffic addressed to targeted devices or zones without affecting other traffic. Within the module, integrated multiple layers of defense enable it to identify and block malicious attack traffic while allowing legitimate transactions to continue flowing to their original destinations.
Cisco Catalyst 6500/Cisco 7600 Anomaly Guard module: A single Cisco Anomaly Guard module allows the platform to process attack traffic at gigabit-per-second line rates. The Cisco Anomaly Guard module employs a unique on-demand deployment model, diverting and scrubbing only traffic addressed to targeted devices or zones without affecting other traffic. Within the module, integrated multiple layers of defense enable it to identify and block malicious attack traffic while allowing legitimate transactions to continue flowing to their original destinations. -
 Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series NAM: The Cisco NAM provides visibility into all layers of network traffic by using Remote Monitoring 2 and other advanced management information bases. The Cisco NAM accesses the built-in Remote Monitoring (mini-RMON) features of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers to provide port-level traffic statistics at the MAC (data link) layer. It also delivers the intelligence required to analyze traffic flows for applications, hosts, conversations, and network-based services, such as QoS and VoIP.
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series NAM: The Cisco NAM provides visibility into all layers of network traffic by using Remote Monitoring 2 and other advanced management information bases. The Cisco NAM accesses the built-in Remote Monitoring (mini-RMON) features of the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches and Cisco 7600 Series routers to provide port-level traffic statistics at the MAC (data link) layer. It also delivers the intelligence required to analyze traffic flows for applications, hosts, conversations, and network-based services, such as QoS and VoIP.
Endpoint Security Solutions
![]() Cisco also has security solutions for endpoint security: the Cisco Security Agent and the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents. The Cisco Security Agent software integrates endpoint server and desktop computers into the Cisco Self-Defending Network. The Cisco Security Agent provides the following services for endpoints:
Cisco also has security solutions for endpoint security: the Cisco Security Agent and the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents. The Cisco Security Agent software integrates endpoint server and desktop computers into the Cisco Self-Defending Network. The Cisco Security Agent provides the following services for endpoints:
-
 Spyware and adware protection
Spyware and adware protection -
 Protection against buffer overflows
Protection against buffer overflows -
 Distributed firewall capabilities
Distributed firewall capabilities -
 Malicious mobile code protection
Malicious mobile code protection -
 Operating system integrity assurance
Operating system integrity assurance -
 Application inventory
Application inventory -
 Audit log consolidation
Audit log consolidation
![]() The Cisco Security Agent identifies and prevents malicious behavior, eliminating known and unknown (“Day Zero”) network threats. The Cisco Security Agent aggregates and extends multiple endpoint security functions by providing intrusion prevention and distributed firewall capabilities in addition to malicious mobile code protection, system integrity assurance, and audit log consolidation. All these capabilities are based on deploying Cisco Security Agents throughout the network and configuring and managing the agents through the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents. The Cisco Security Agent also provides important endpoint information to the Cisco Security MARS to enhance threat identification and investigation across the network. The Cisco Security Agent integrates with Cisco NAC and NAC Appliances with trusted QoS to improve the delivery of mission-critical traffic when the network is under a heavy load.
The Cisco Security Agent identifies and prevents malicious behavior, eliminating known and unknown (“Day Zero”) network threats. The Cisco Security Agent aggregates and extends multiple endpoint security functions by providing intrusion prevention and distributed firewall capabilities in addition to malicious mobile code protection, system integrity assurance, and audit log consolidation. All these capabilities are based on deploying Cisco Security Agents throughout the network and configuring and managing the agents through the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents. The Cisco Security Agent also provides important endpoint information to the Cisco Security MARS to enhance threat identification and investigation across the network. The Cisco Security Agent integrates with Cisco NAC and NAC Appliances with trusted QoS to improve the delivery of mission-critical traffic when the network is under a heavy load.
![]() As discussed earlier, the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents provides all management functions for all agents in a centralized manner. Its role-based web browser access makes it easy for administrators to create agent software distribution packages, create or modify security policies, monitor alerts, or generate reports. The Management Center ships with more than 20 fully configured default policies, making it easy for administrators to deploy thousands of agents across the enterprise. It also allows customers to deploy agents in IDS mode, in which alerts are generated for suspicious activities, but traffic is not blocked.
As discussed earlier, the Management Center for Cisco Security Agents provides all management functions for all agents in a centralized manner. Its role-based web browser access makes it easy for administrators to create agent software distribution packages, create or modify security policies, monitor alerts, or generate reports. The Management Center ships with more than 20 fully configured default policies, making it easy for administrators to deploy thousands of agents across the enterprise. It also allows customers to deploy agents in IDS mode, in which alerts are generated for suspicious activities, but traffic is not blocked.
 Securing the Enterprise Network
Securing the Enterprise Network
![]() Securing the enterprise network involves deploying technologies that support identity and access control, threat defense and infrastructure protection, and security management. This section reviews the locations at which security devices and solutions might be deployed within the Enterprise network of a sample organization.
Securing the enterprise network involves deploying technologies that support identity and access control, threat defense and infrastructure protection, and security management. This section reviews the locations at which security devices and solutions might be deployed within the Enterprise network of a sample organization.
Deploying Security in the Enterprise Campus
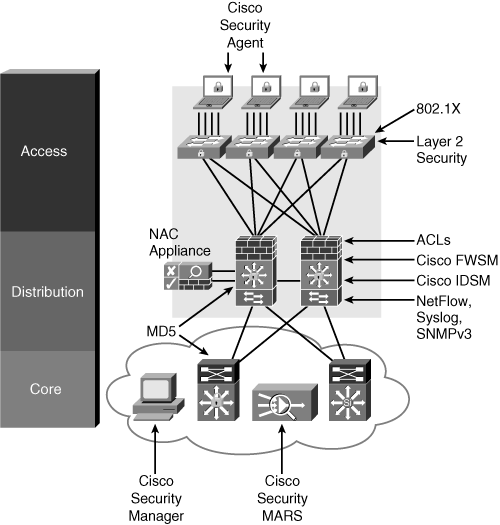
![]() Consider an organization that has experienced several incidents in which laptop users on the campus network have brought in viruses from home, some users have attempted to intercept network traffic, and some interns have tried to hack the network infrastructure. To manage the risks, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-21 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Campus.
Consider an organization that has experienced several incidents in which laptop users on the campus network have brought in viruses from home, some users have attempted to intercept network traffic, and some interns have tried to hack the network infrastructure. To manage the risks, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-21 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Campus.
![]() Identity and access control technologies include the following:
Identity and access control technologies include the following:
-
 802.1X port security and/or NAC for user endpoints
802.1X port security and/or NAC for user endpoints -
 NAC appliances
NAC appliances -
 ACLs on Cisco IOS devices
ACLs on Cisco IOS devices -
 Firewalls (for example, Cisco FWSM) provide stateful inspection and application inspection
Firewalls (for example, Cisco FWSM) provide stateful inspection and application inspection
![]() Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
-
 NetFlow
NetFlow -
 Syslog
Syslog -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 HIPS (for example, the Cisco Security Agent)
HIPS (for example, the Cisco Security Agent) -
 NIPS
NIPS -
 Cisco Security MARS
Cisco Security MARS -
 Cisco Security Manager
Cisco Security Manager
![]() Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
-
 AAA
AAA -
 SSH
SSH -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security
IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security -
 Layer 2 security features
Layer 2 security features
![]() Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.
Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.
Deploying Security in the Enterprise Data Center
![]() The organization’s data center hosts servers for the main campus network and branch offices. These servers contain the enterprise’s most sensitive information and are available to a large number of users. Network performance is a critically important issue, which sometimes limits the choice of protection mechanisms. Some specific risks in the data center include direct compromise of exposed applications and unauthorized access to data, and compromise of other hosts from compromised servers in this module.
The organization’s data center hosts servers for the main campus network and branch offices. These servers contain the enterprise’s most sensitive information and are available to a large number of users. Network performance is a critically important issue, which sometimes limits the choice of protection mechanisms. Some specific risks in the data center include direct compromise of exposed applications and unauthorized access to data, and compromise of other hosts from compromised servers in this module.
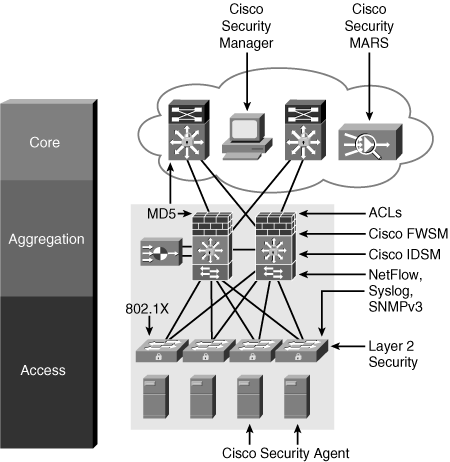
![]() To provide security, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-22 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Data Center.
To provide security, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-22 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Data Center.
![]() Identity and access control technologies include the following:
Identity and access control technologies include the following:
-
 802.1X port security
802.1X port security -
 ACLs on Cisco IOS devices
ACLs on Cisco IOS devices -
 Firewalls (for example, Cisco FWSM)
Firewalls (for example, Cisco FWSM)
![]() Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
-
 NetFlow
NetFlow -
 Syslog
Syslog -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 IDS (for example, the Cisco IDSM-2)
IDS (for example, the Cisco IDSM-2) -
 NIPS
NIPS -
 Cisco Security MARS
Cisco Security MARS -
 Cisco Security Manager
Cisco Security Manager
![]() Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
-
 AAA
AAA -
 SSH
SSH -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security
IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security -
 Layer 2 security features
Layer 2 security features
![]() Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.
Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.
Deploying Security in the Enterprise Edge
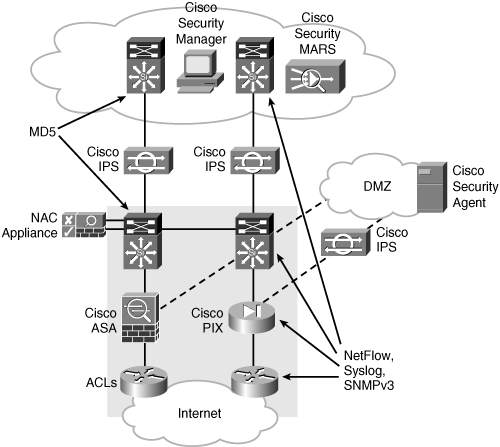
![]() The enterprise edge modules provide WAN connectivity among various parts of the enterprise network. Security is important whenever data is transferred between locations. For example, some specific risks in the WAN module include the following:
The enterprise edge modules provide WAN connectivity among various parts of the enterprise network. Security is important whenever data is transferred between locations. For example, some specific risks in the WAN module include the following:
-
 Data transmission confidentiality and integrity violations, in which an attacker who obtains physical access to the network media or to a service provider WAN switch can intercept WAN traffic and might eavesdrop or change data in transit.
Data transmission confidentiality and integrity violations, in which an attacker who obtains physical access to the network media or to a service provider WAN switch can intercept WAN traffic and might eavesdrop or change data in transit. -
 Accidental or deliberate misconfiguration of the WAN network, which can result in the interconnection of different enterprises. Some WAN protocols might establish automatic peering, and unwanted connectivity could become possible.
Accidental or deliberate misconfiguration of the WAN network, which can result in the interconnection of different enterprises. Some WAN protocols might establish automatic peering, and unwanted connectivity could become possible.
![]() To provide security, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-23 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Edge.
To provide security, the organization implements identity and access control solutions, threat detection and mitigation solutions, infrastructure protection, and security management. Figure 10-23 illustrates where various security technologies might be deployed within the Enterprise Edge.
![]() Identity and access control technologies include the following:
Identity and access control technologies include the following:
-
 ACLs on Cisco IOS devices
ACLs on Cisco IOS devices -
 Firewalls (such as Cisco PIX Security appliances)
Firewalls (such as Cisco PIX Security appliances) -
 IPsec or SSL VPNs
IPsec or SSL VPNs -
 NAC appliances
NAC appliances -
 ASA appliances
ASA appliances
![]() Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
Threat detection and mitigation technologies include the following:
-
 NetFlow
NetFlow -
 Syslog
Syslog -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 NIPS
NIPS -
 Cisco Security MARS
Cisco Security MARS -
 Cisco Security Manager
Cisco Security Manager
![]() Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
Infrastructure protection technologies include the following:
-
 AAA
AAA -
 SSH
SSH -
 SNMPv3
SNMPv3 -
 IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security
IGP or EGP MD5 routing protocol security
![]() Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.
Security management technologies include Cisco Security MARS and Cisco Security Manager.




1 comments
Cloud Ace Technologies is offering Implementation Services on Cloud Computing, Cloud Services, IT Security, Storage solutions
IT Security Solutions
Post a Comment